As cloud computing becomes more common, it’s essential for CTOs and other technical decision-makers to understand the various cloud deployment options available.
Organizations leverage cloud computing to cut down on infrastructure expenses, boost scalability, flexibility, and agility. Cloud deployment models offer a range of options tailored to fit specific business requirements. This article will explore the 5 types of cloud deployment models, analyze their advantages and disadvantages, and highlight their distinctions.
What is a Cloud Deployment Model?
A cloud deployment model represents the particular category of cloud environment based on who controls security, who has access to the data, and whether the resources are shared or dedicated. The cloud deploymen t model also defines the purpose and nature of your cloud environment. Each cloud deployment model can satisfy different needs of the organization and you need to know the right cloud deployment model that fits within your organization’s methodology.
Types of Cloud Deployment Models
The concept of cloud deployment models categorizes various types of cloud environments based on factors like ownership, scale, access, as well as the characteristics and objectives of the cloud. It essentially determines where the servers you’re using are located and who has control over them. These deployment models outline the structure of your cloud infrastructure, the extent of customization available, and whether you’ll receive pre-made services or need to build everything from scratch. Additionally, they define the relationships between your infrastructure and the users of your cloud. Below, we’ll describe various kinds of cloud computing deployment models.
1. Private Cloud Deployment Model
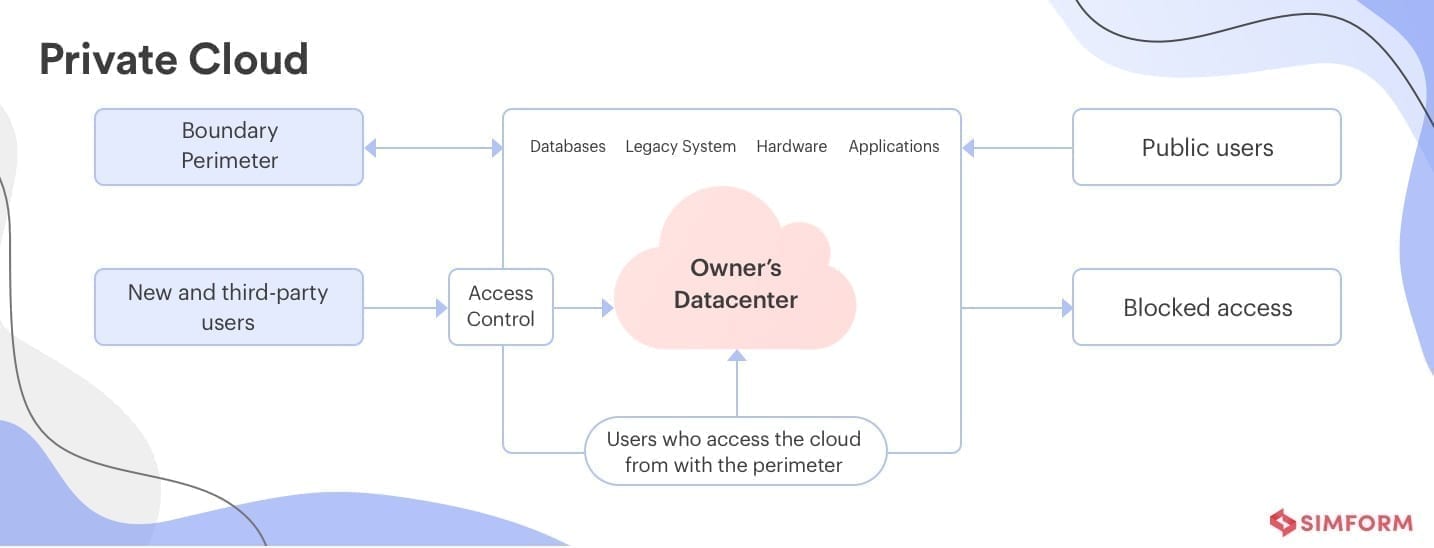
The private cloud model is the antithesis of the public cloud deployment model. It’s designed to be used only by one organization so you are not required to permit others to use the cloud’s infrastructure. Essentially, how the hardware is controlled distinguishes a private cloud from a public cloud. A private cloud is sometimes referred to as an “internal cloud,” and it denotes having access to systems and services within a certain company or region.
This cloud platform is set up in a secure cloud environment that is guarded by powerful firewalls and managed by an organization’s IT department. You have more control over how cloud resources are used while using the private cloud.
Private cloud costs are not pay-as-you-go; you must pay for the entire stack, whether or not you use it. You may still select a record meter that displays use to various user groups or renters. “Chargeback” is the term for this payment method facilitated by a private cloud.
Advantages of private cloud
- The company is the exclusive owner with full control of its service integrations, operations, regulations, and user practices.
- It supports legacy applications, which is not an option on a public cloud.
- Only authorized personnel are given access, which is ideal for protection of corporate data with a privacy policy.
- Companies can customize their solution according to demands.
- It further enhances the quality of service given by the clients.
- It offers exceptional reliability in performance.
- It provides higher control over system configuration as per your company’s requirements.
Disadvantages of private cloud
- Under-utilization is a cost to your company, and not to your provider, affecting the model’s overall feasibility.
- Your company may need to invest in expensive hardware and software along with trained human resources.
- Scalability depends on the choice of hardware.
- It’s maintained in-house and demands high maintenance.
- A hosting-service provider may encounter limitations with storage capacity, which can influence your requirements directly.
Private cloud: possible customer scenario of central government
A nation’s government may be searching for a more secure cloud model if it uses thousands of computers to support the infrastructure of its ministries. The central government might use a private cloud that has a private network to host many government applications including payroll, personnel management, back-office systems, and accounting while keeping their infrastructure secure and controlled in a private cloud server.
How to Build a Scalable Application up to 1 Million Users on AWS
2. Public Cloud Deployment Model
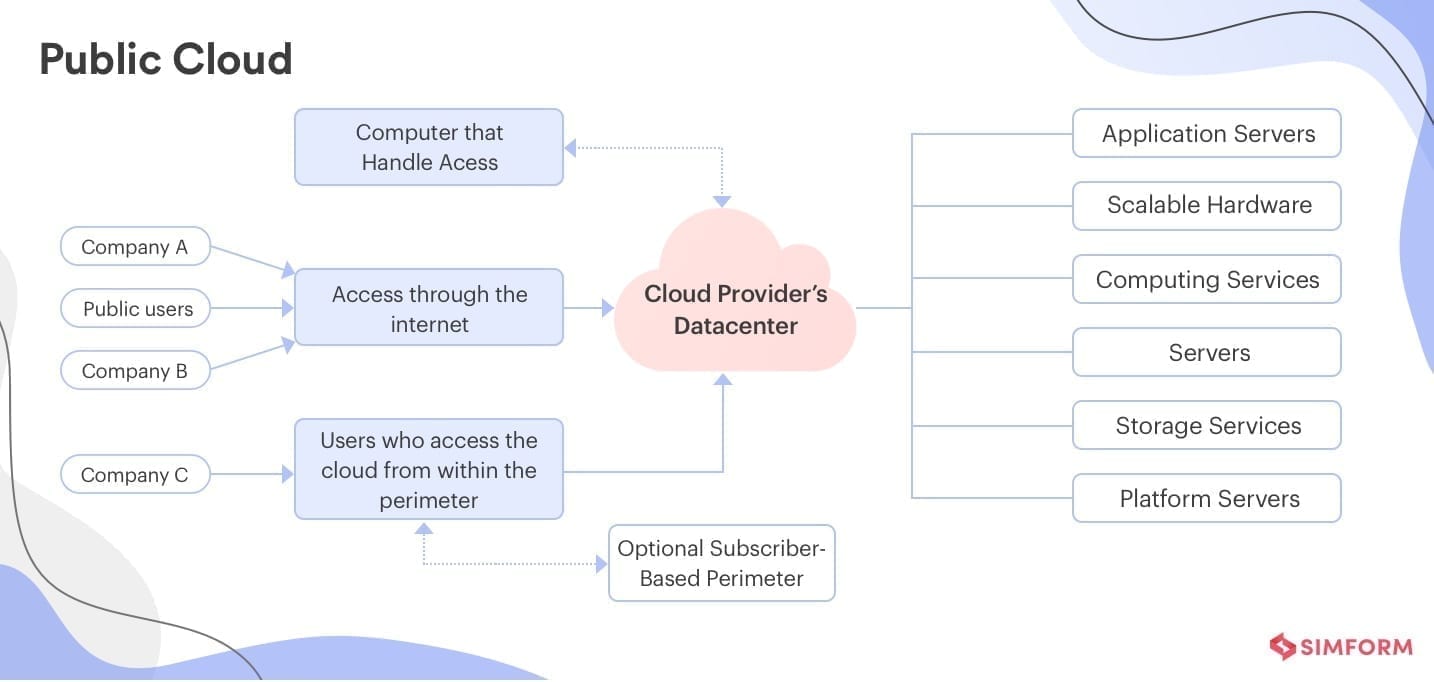
A “public cloud” is a term used to describe when external suppliers make their services available across an unrestricted public server network. In a public cloud model you and other customers of the same provider share the same hardware(third-party servers), software, and network resources.
Who is in charge of hosting and managing the cloud is another significant distinction between a public cloud offering and a private cloud. As you are merely “renting” space from a third-party provider in a public cloud, the provider is responsible for funding and maintaining the whole physical infrastructure or server network. You don’t have to worry about the management in the public deployment model as a customer who pays for this service. You only use it to store your data and access pay-as-you-go services.
Of all the cloud deployment types, public clouds are the most affordable investment since you don’t need to purchase pricey IT resources (as opposed to other clouds).
Advantages of public cloud
- It’s the most affordable model on the market with no location dependencies or resource procurement hassles.
- You don’t need infrastructure management with a dedicated in-house team to fully use a public cloud.
- It offers greater vertical scalability through virtualization.
- It’s very reliable, so there’s no interruption in your networking services, available resources or scope of any failure.
- Services like SaaS, Paas, and Iaas along with other computing resources can be readily accessed on the public cloud via all internet-enabled devices.
Disadvantages of public cloud
- Shared resources sometimes lead to breakdowns in scalability and flexibility.
- It’s not suitable for data-sensitive applications.
- Concerns around its security and privacy are serious. It attracts more targeted attacks as it has no stringent data protocol.
- The public cloud has limited customization. Clients can select the operating system and the VM size but cannot customize orders, reports, or networking.
Public cloud: prospective customer scenario for eCommerce applications with dynamic resource requirements
Let’s say an e-Commerce application that manages an online store has an increase in traffic and sales around the holidays. Yet, because they have limited resources available, they don’t want to restrict customer service or the shopping experience for their customers. In this scenario, they can choose to rent a public cloud to manage these fluctuating resource requirements in their systems. By availing of a public cloud infrastructure, the company can:
- Run robust operations without spending money on their own infrastructure
- Ensure scalable performance as required
- Benefit from a pay-as-you-go payment system that keeps their finances in check.
Moreover, an application’s mobility is not at all an issue while working with a public cloud. Without compromising the responsiveness or performance of the e-store overall, the corporation may quickly transition to VM if they wish to use a different cloud model.
Thinking to migrate your application to Cloud?
3. Community Cloud Deployment Model
 This model is shared among many companies/tenants operating within the same domain like banking, government, education institutions, etc. Access to a community cloud is limited to the members of that specific community. In other words, a group of several companies shares a multi-tenant setup where they have some privacy, security, and performance limitations and concerns.
This model is shared among many companies/tenants operating within the same domain like banking, government, education institutions, etc. Access to a community cloud is limited to the members of that specific community. In other words, a group of several companies shares a multi-tenant setup where they have some privacy, security, and performance limitations and concerns.
Businesses use this for joint ventures and research firms that require a centralized cloud-computing system. For governments, it’s known as Government Cloud and is embraced by many countries. Due to legislative issues, a typical Government Cloud is the answer to many country-specific judicial matters.
For example, according to Google‘s recent announcement, it will develop security-and-app-management tools for the Defence Innovation Unit of USA’s Pentagon to eliminate the challenges the Defense Department faces and run a multi-cloud environment in a community cloud deployment model. Two Google Cloud product managers, Christopher Johnson and Bhavna Batra, said, “Assured Workloads for Government helps its customers, suppliers, and contractors.
Additionally, the Department of Defense, the FBI’s Criminal Justice Information Services Division, and the Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program to meet the extraordinary security and compliance standards set forth.”
Community cloud is technically no different than public cloud or private cloud. The difference lies in who holds the control together with their set of users. It’s as if a group of companies shared the cost of a building, and several other firms with similar requirements for infrastructure and resources share this environment.
In this model, all active users share the cost. This multi-tenant data center helps companies boost their efficiency and performance while also maintaining standard protocols for privacy, security, management, implementation, and usage for projects like a centralized cloud.
Advantages of community cloud
- It’s more cost-effective than other cloud models. Multiple companies share the bill, which lowers the individual cost.
- It offers scalability and flexibility to manage cloud computing needs.
- Configuration and protocols in community systems are designed to meet the community’s requirements to enhance efficiency.
- The availability and reliability of the community make it a go-to choice for governments and universities.
Disadvantages of community cloud
- The most common problem with this system is its lower bandwidth capacity with limited storage.
- Its security standards are difficult to maintain without skilled IT staff.
- It increases the setup costs and incurs consistent maintenance costs.
- You can’t get the complete benefits of either private or public cloud.
Community cloud: prospective customer scenario for a large organization payroll processing
Say there is a large organization that has two dedicated servers for payroll processing, which became a complicated and time-consuming process over the years. Now they are considering simplifying it, so they decide to migrate it to a cloud model. Their existing payroll-system architecture was a distributed application. So currently, to manage employee data and utilize cloud-database service from SQL database, they have to retrieve data from cloud storage.
In order to simplify their payroll app and make this process faster, they want to deploy their app to four different VMs to run simultaneously. Here, the community cloud deployment model is best suited, according to their organization’s requirements.
Solving problems: The overall payroll processing time was delaying their operations and created many time-consuming bottlenecks. This community cloud model could resolve this and transform it into a flexible, faster, and cost-effective solution. This cloud model could also be useful if the organization expands in the future.
Requirements and capabilities: In this scenario, the cloud services could utilize VMs cloud storage like IaaS. To opt for a community cloud model, they don’t want to modify the existing payroll app, and are considering deploying it to VMs instead. Furthermore, to avoid conflicts with data structures, the database can also be migrated to the cloud.
Portable concerns: If the organization wants to migrate again, they can do so according to their cloud storage provider’s services and technical capabilities.
Cloud Cost Optimization Strategies (Even AWS won't Tell you!)
4. Hybrid Cloud Deployment Model
The hybrid deployment model consists of two or more cloud-deployment models. They’re all unique, but they’re bound by specific, standard protocols. Very few companies can switch over all of their technology stacks to the cloud in one go. For such companies, the hybrid cloud-deployment model provides a smoother transition with a mix of on-premise and cloud options.
NASA uses this system. For example, Nebula- an open-source cloud-computing project, employs a private cloud for research and development while using a public cloud to share datasets with external partners and other people.
Hybrid cloud models are used for cloud bursting. Say the client runs their application mainly in a private cloud. But if the system is experiencing a spike, sudden surge, or heavy load, it can ‘burst’ into the public cloud to ease the load. This hybrid cloud combination of public and private cloud environments allows sharing of applications. It helps companies seamlessly scale services within their cloud infrastructure whenever required.
This model safeguards and strategically controls your company’s essential assets. It’s such a cost-effective and resource-positive approach that more companies should adopt it. Its infrastructure strategy facilitates application and data portability greatly and enables companies to mix and match options that best suit their requirements.
As the private cloud-deployment model might not be optimal for all workloads, this model meets all requirements of even the larger organizations. It borrows significant advantages of both public and private cloud although some companies find their needs met via either one model and embrace the benefits to going “all in”.
Advantages of hybrid cloud
- It reduces operational costs and gives companies the freedom to combine cloud models for workflows.
- Thanks to its segmented storage, the security protocols are simpler. So it becomes easy to shield the cloud from attackers.
- It gives robust setup flexibility, so that customers can customize their solutions to fit their requirements.
- It’s scalable due to its mix-and-match combination to operate and manage the workloads.
Disadvantages of hybrid cloud
- It’s a somewhat complex setup to manage as you combine two or more separate cloud models.
- It makes sense only if your company has varied use or demand for managing the workloads.
- It’s noticed that there can be infrastructure dependency on this model.
- There are possibilities of a security violation by public cloud back-door.
Hybrid cloud: possible customer scenario for a local government
To address the concerns of multiple states or local administrations, this model might fit right in. Say, a central government is looking to centralize yet build a hybrid cloud environment for their cloud ecosystem. To handle local administration data storage needs for sensitive information and to manage internal tasks. A hybrid cloud deployment model can resolve this problem.
Solving customer problems: The local administrations could store their confidential data and economize their energy consumption with fewer dedicated IT staff.
Requirements and capabilities: In case if a central government’s privacy laws are strict about adhering to storing and accessing data from a server. This hybrid cloud model might resolve their challenge within their compliances, capabilities, and already existing cloud infrastructure.
Portability concerns: Portability is not a concern because the government might have no intention of moving its centralized applications and data.
5. Multi-cloud Model
Around 60% of IT experts and business executives utilize several clouds, and 47% are increasing their use of multiple clouds. In the Multi-cloud Model, as the name suggests, we’re talking about using numerous cloud providers simultaneously. It is comparable to the hybrid cloud deployment strategy, which mixes resources from both public and private clouds. Multi-cloud utilizes numerous public clouds as opposed to combining private and public clouds. Cloud services may experience an outage. Even a small outage can lead to a loss of millions of dollars for enterprises relying on these cloud services.
This is the reason why many organizations prefer to go with the multi-cloud deployment model which has multiple databases. This ensures that a data outage in one database does not affect the data stored in another database.
Thus the main reason why organizations go with the multi-cloud strategy is to increase the availability of their cloud infrastructure. This is because it is rare that two public cloud services will experience an outage simultaneously.
Advantages of the Multi-Cloud Model
- The ability to utilize the strengths of different cloud providers for various applications, tasks, and business needs.
- Reduced latency and improved user experience by selecting cloud locations that are near customers.
- Increased reliability of services as it is unlikely for two separate clouds to experience an outage at the same time.
Disadvantages of the Multi-Cloud Model
- Incurs additional cost for moving data between clouds.
- Requires the development and maintenance of multiple deployment and pipeline strategies.
- Complex cloud architecture can lead to difficulties in monitoring and troubleshooting systems.
Multi-cloud: possible customer scenario of a healthcare institute
By implementing a multi-cloud strategy, healthcare solutions providers operating in multiple locations can ensure high reliability as it is rare that all the public cloud systems fail at the same time. Given the sensitive nature of their business, it is crucial for these organizations to have a highly dependable system and a multi-cloud approach can provide that.
Problem to address: By implementing a multi-cloud strategy, healthcare organizations can ensure high reliability by utilizing multiple public cloud systems. This approach allows them to increase bandwidth, improve network performance by bringing deployments closer to customers, and integrate new data sources from various cloud providers while still maintaining low-latency access to their data through multiple cloud workloads.
Requirements and capabilities: By constructing their entire cloud infrastructure on two public cloud systems, the healthcare organization can ensure an always-on architecture for servers and databases.
Portability concerns: By adopting a multi-cloud strategy, the organization can increase its portability by enabling greater flexibility in the deployment and execution of workloads and data across different cloud environments.
Cloud Deployment Models Chart of Comparative Overview:
| Parameters | Pubic Cloud | Private Cloud | Community Cloud | Hybrid Cloud | Multi Cloud |
| Ease of setup | Very easy to setup | Very hard to setup as your team creates the system | Easy to setup because of community practices | Complex to setup due to interconnected systems | Complex to setup as there are multiple public clouds that one needs to integrate |
| Ease of use | Very easy to use | Complex and requires an in-house team | Relatively easy to use as the members help solve problems and protocols | Difficult to use if the system is not setup properly | Difficult to use if the system is not integrated properly |
| Data control | Low- the provider has complete control of date | Very high- ownership is with the user | High- if members collaborate | Very high- with right setup | Low- providers have complete control |
| Reliability | Prone to outages and failures | High with the right team | Depends on the community policy | High- with the right setup | High- as there is a rare chance of the simultaneous failure of all public cloud systems |
| Scalability | High | Limited- as need to invest in physical infrastructure if one wants to scale up the system. | Fixed capacity tends to limit the scalability of the system | High- with right setup | High- with the right setup |
| Cost | Inexpensive | Very expensive | Members share cost | Cost-effective | Increased cost as compared to the hybrid model as we have to move the data between clouds and have to procure the services of two cloud service providers |
| Demand for in-house hardware | No | yes | No | In-house hardware is not a necessity | In-house hardware is not a necessity |
Take Away
As you navigate the realm of cloud deployment options, don’t forget to assess your application architecture’s compatibility with the chosen model. Upgrading your architecture and aligning it with the right cloud deployment will be a strategic move for your organization’s future.
Selecting the optimal deployment option is paramount for your company’s success. A thorough understanding of the advantages and disadvantages of each model empowers you to make informed decisions that drive efficiency and growth.
To explore how our expert team at Simform can assist you in making the best cloud deployment choices for your business, please don’t hesitate to contact us
Still struggling with selecting the perfect cloud deployment model? We’re here to help!
The cheapest cloud deployment model varies based on usage patterns and cloud service providers. Generally, Public Cloud options are cost-effective for organizations seeking budget-friendly solutions.
The most popular cloud computing deployment models are Public Cloud and Hybrid Cloud. Public Cloud provides easy accessibility, while Hybrid Cloud combines flexibility with data control.
The best cloud deployment model for your organization depends on factors such as data sensitivity, compliance needs, scalability demands, and budget constraints. Conduct a thorough assessment to determine the ideal fit.