When you want to deliver your product through microservices, adopt an established microservices framework from the start to make things easier. A framework is a ready-made architectural structure for application development. It helps form the shape of your software as it lives on your infrastructure, offers teams clarity and focus, and has tools to help with development. Best of all, a framework saves you time in planning, development, and support.
There are different frameworks available based on the project’s needs. Java, Python, C++, Node JS, and .Net are a few languages for developing microservices. The selection of a microservice framework depends on several factors, such as the maturity of the community, ease of development, learning curve, architecture support, support of automation, independent deployments, and continuous integration. Let’s dive into popular microservices frameworks, their features, and a checklist to select the right framework for your application.
Popular Microservices Frameworks
1. Spring Boot
Spring Boot powered by Spring Cloud, is the modern and most used Java microservices framework to build microservices. It allows developers to build a software architecture in self-contained components that give your code resilience and flexibility. It has 69.7k stars on GitHub, and its popularity is rising, with no real competitors nearby to beat the stats.
Developers starting with this microservices framework can quickstart their applications using Spring Initializr and then package them as a JAR. Its embedded server model allows rapid development, which leads to shorter time-to-market for modern applications. However, when many applications are in production, Spring Boot isn’t an ideal choice of framework.
Moreover, microservices’ distributive nature poses a challenge for developers to maintain different components simultaneously. Spring framework addresses this with an architectural style that has several ready-to-run cloud patterns under Spring Cloud. Cloud gives resilience to an application, and with Spring Cloud, we get the advantage of service discovery, circuit breaker, load balancing, monitoring, and distributive tracing.
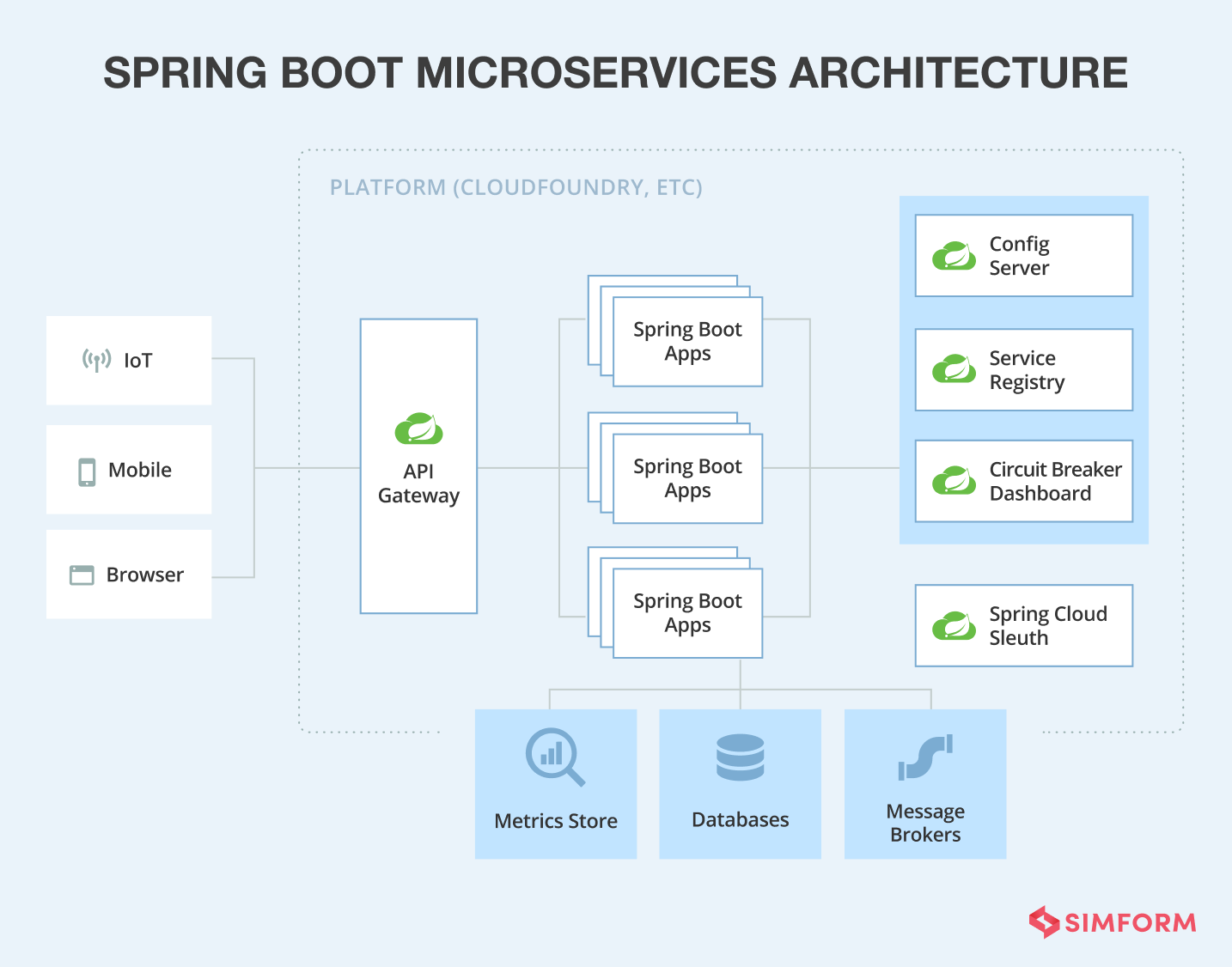
Key Benefits:
- Allows development of reactive microservices applications with rest API using Spring MVC.
- Easy to integrate with leading frameworks owing to its Inversion of Control.
- Comes with an optional instrumental framework ‘Micrometer’ for monitoring valuable metrics, distributed tracing, and insights.
- Utilizes Cloud Foundry for horizontal scaling and connecting multiple backend services at ease.
- Improved time-to-market for complex application architecture.
2. Golang
Go programming language is popular amongst developers specializing in microservices for its Google-backed support and services. With GoKit and GoMicro, which are designed explicitly to create microservices on Golang, one can easily build a distributed architecture for any application. It’s an excellent microservices framework to create REST and gRPC (Google Remote Procedure Call) protocols that let different services communicate seamlessly.
One of the easiest ways to develop microservices using Go is with GoMicro. It is a pluggable PRC library that provides the fundamental building blocks of microservices application development. Even though it’s not a framework per se, it addresses the challenges of a distributed architecture and offers simple abstractions.
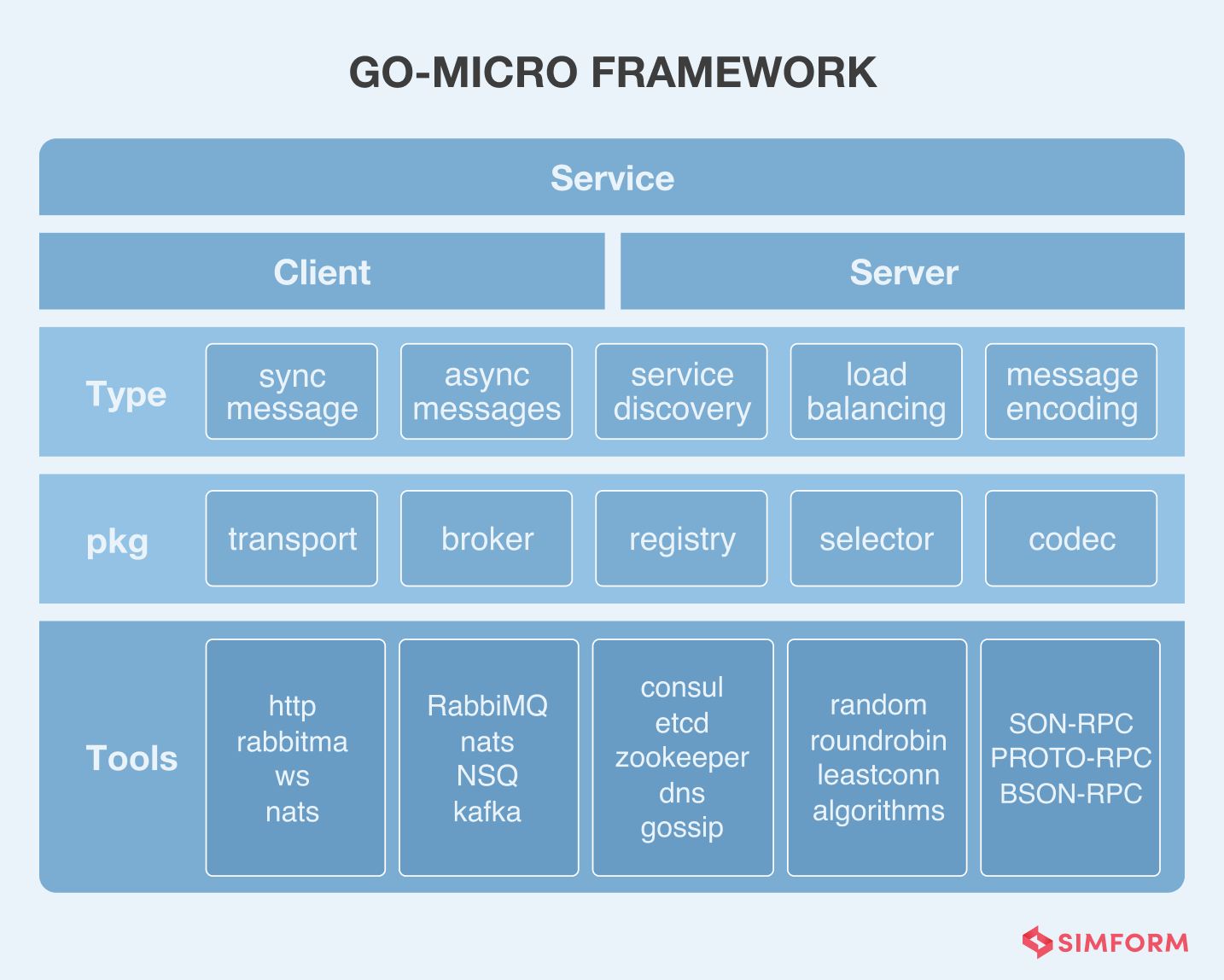
Another way is to use GoKit- a programming tool kit for creating microservices in Go. It is a zip containing co-related packages that build a framework to build service-oriented applications. It can easily integrate JSON over HTTP, allowing it to integrate with standard infrastructural components.
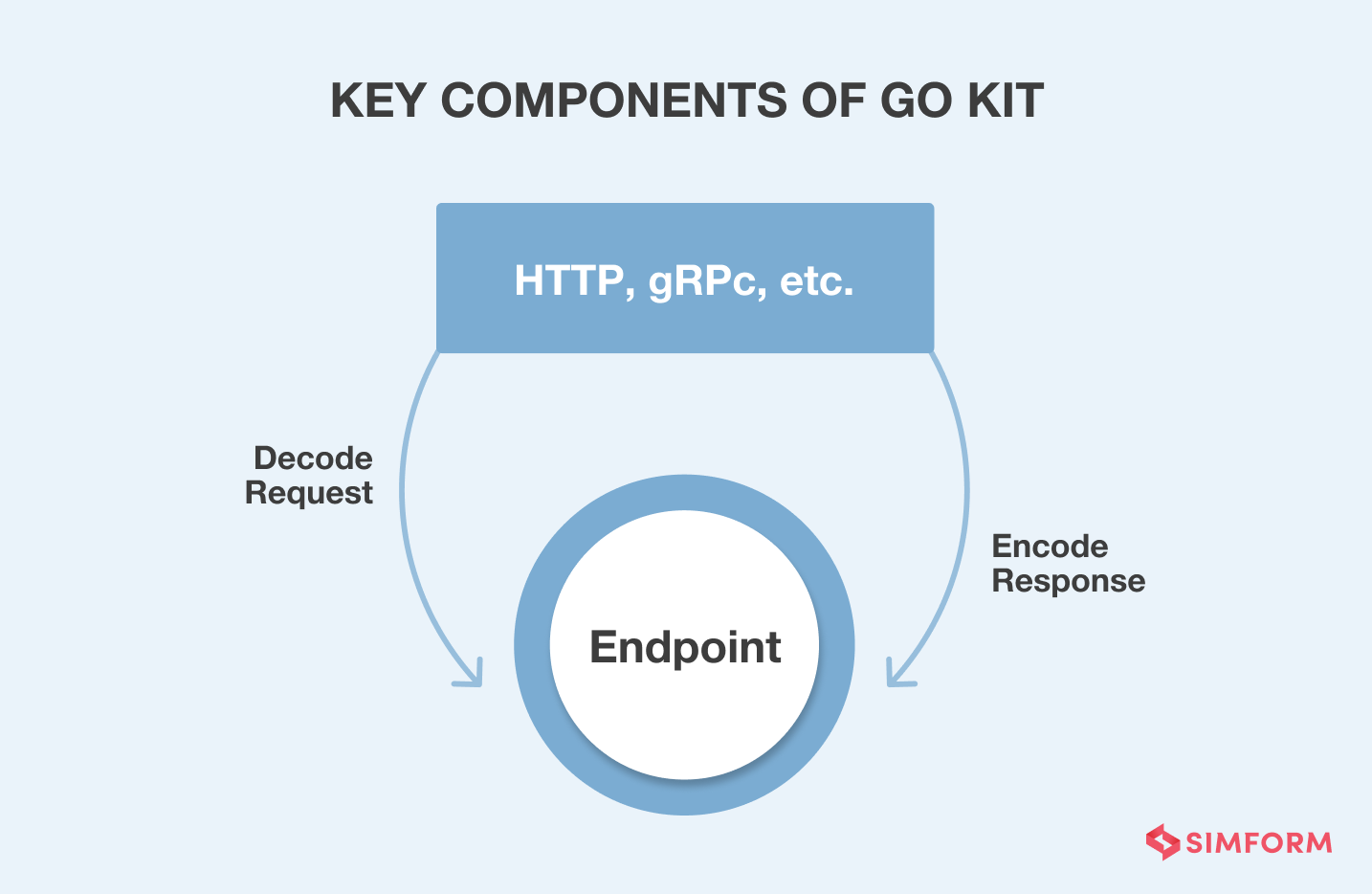
Key Benefits:
- The framework reduces friction while deploying applications and promotes interoperability.
- A pluggable toolkit that can be used by developers utilizing Go for app development.
- Ready pre-defined templates for an easy start.
- A web dashboard for exploring services and raising queries.
- Easily testable microservice architecture supporting robust and complex apps.
3. Eclipse Vert.X
When you need an event-driven microservices framework to develop applications, then choose Eclipse Vert.X. It is a polyglot framework that supports Java, JavaScript, Ruby, Groovy, Kotlin, Scala, and Ceylon. Also, it runs on a Java Virtual Machine, which makes it a favorable choice for complex applications with a service-oriented architecture.
Compared to traditional stacks and frameworks based on blocking I/O, Vert.X, built by Eclipse Foundation, has resource-efficient features that simultaneously handle many requests. It can execute tasks in a constrained environment, especially in containers. Vert.X microservice framework is popular for its flexibility in composability and embedded characteristics, making it a highly scalable toolkit than a framework.
Vert.X’s ecosystem consists of Web APIs, databases, event streams, messaging, cloud, security features, registries, and several other elements. Being an open-source framework also gives developers the advantage to add new features from a pre-made repository.
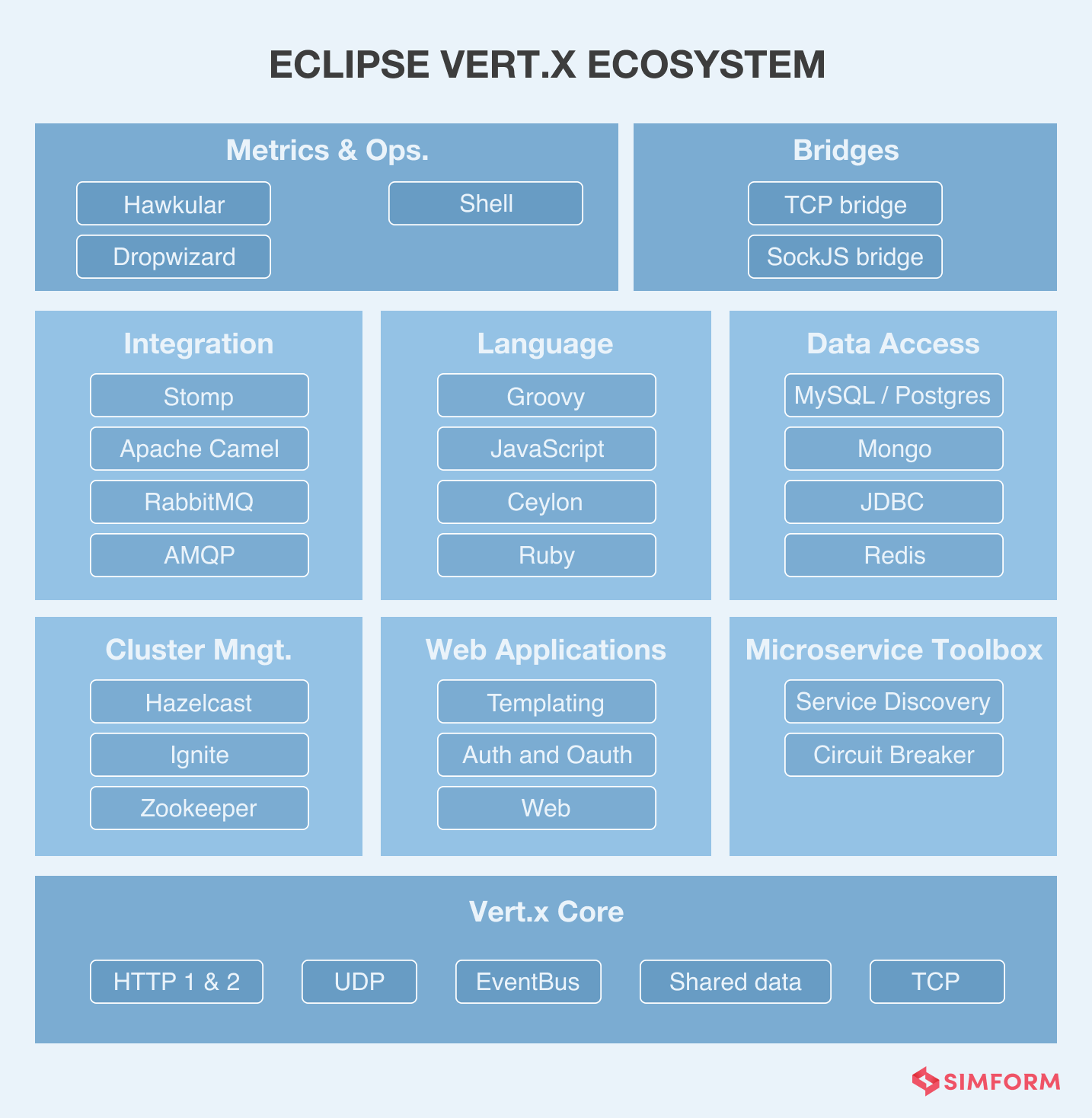
Key Benefits:
- It is lightweight – with a core of 650kb.
- It is a modular framework that allows developers to add bits as much as needed without adding anything extra.
- Health checks can be easily performed through Vert.X web or an event bus.
- Vert.XUnit runs asynchronous unit tests with a polyglot API.
- It has a gPRC support that aligns with Google’s programming style.
4. Quarkus
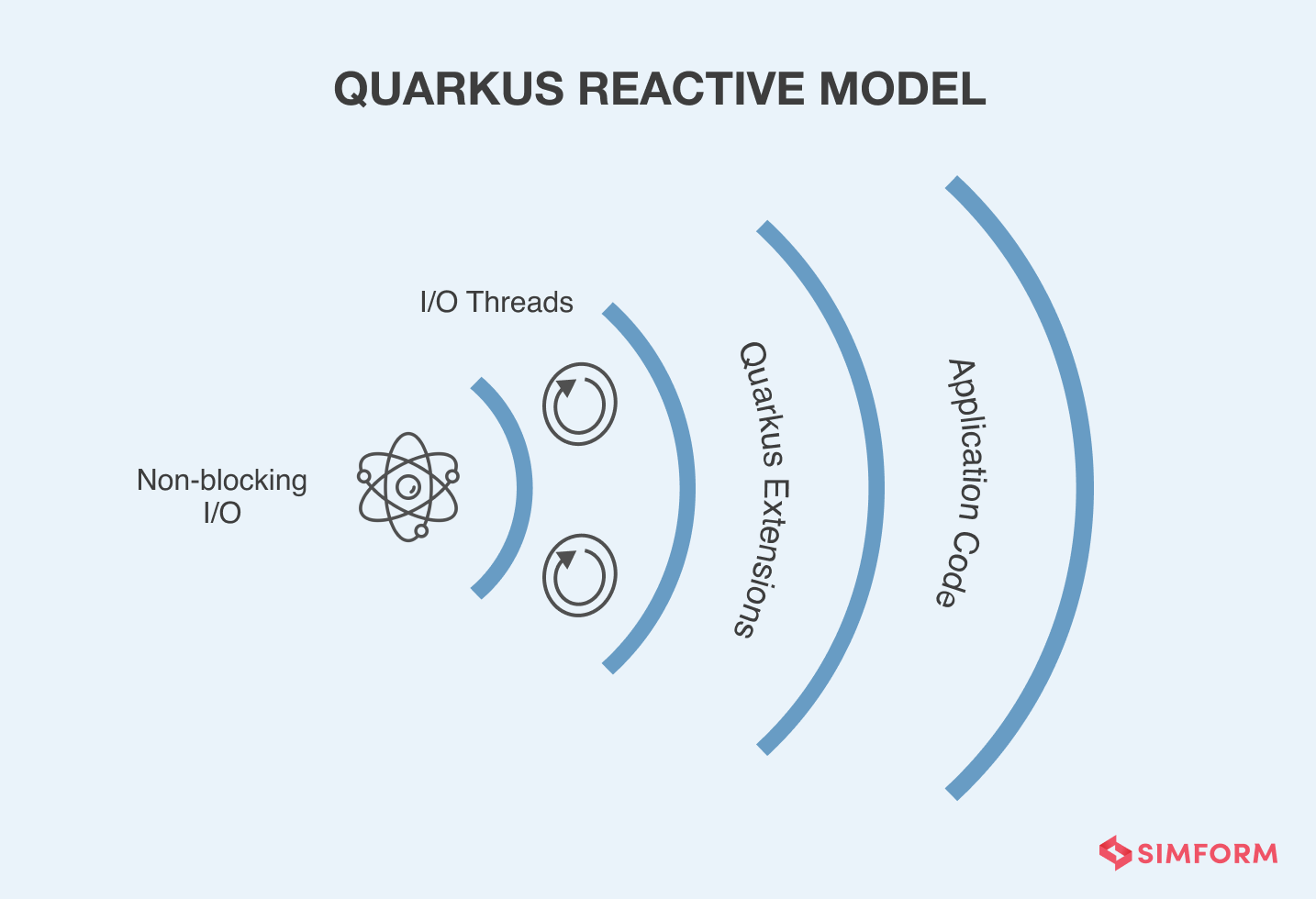
Kubernetes fans vouch for this microservices framework! Quarkus is a Kubernetes native Java framework by Red Hat, specially designed for OpenJDK HotSpot and GraavalVM. The framework offers a reactive and imperative programming model to address the challenges associated with microservices architecture.

Quarkus is a container-first, Kubernative native framework created to optimize low memory usage and fast startup time for developers (tens of milliseconds). The fast startup time enables automatic scaling of microservices on containers and Kubernetes. Meanwhile, low memory usage allows container density optimization within microservices, which have multiple containers deployed independently. But, amateur developers are wary of this framework because of its complicated GraamVM installation and verification of OS-specific binaries.
Moreover, Quarkus development model integrates well to develop HTTP microservices, reactive applications, message-driven microservices, and serverless architecture systems. Developers’ productivity is highly improved with their minimalist features and highly intuitive system that gives them the space to focus on the business aspect of the entire application. Unified configurations, live coding, DEV UI, and continuous testing also boost developers’ experience to create the best microservices.
Key Benefits:
- Has a vast ecosystem of technologies, libraries, and APIs, making it easy to learn and use.
- It is an Ahead-of-Time compilation platform that optimizes code for JVM and native code for improving app performance.
- Boasts of faster boot time compared to other container-first frameworks.
- Low RSS memory and high-density memory utilization.
- Independently deployable guide available for Azure, OpenShift, AWS, Google Cloud.
5. Micronaut
Micronaut is a JVM-based full-stack framework which is a top choice among the popular polyglot frameworks to build modular and microservices applications. The founders’ aim was pretty simple – instead of integrating the right tool kits, build a full-stack environment with all the necessary built-in features necessary for microservices architecture.
Additionally, Micronaut’s start time and memory consumption are not bound to the size of the codebase. This results in an increased speed in start-up time, fast throughput, and a minimal memory footprint. While it sounds convenient, the framework has specific standards that are different from others in the software development industry.
Configurations in Micronaut are quick, making it easy to choose and create your own data-access layer or import external APIs. It has a simple compile time with an aspect-oriented API that does not use reflection. But, remember that Micronaut does not support a lot of cache providers – except for Caffeine and Redis – so if you are depending on caches other than this, you might want to rethink using the framework.
Key Benefits:
- Apps start within tens of milliseconds with GraalVM.
- A smooth learning curve for new developers, utilizing the universal standards for coding.
- An open-source technology that boosts productivity with improved runtime and memory utilization.
- Ease in unit testing that runs instantaneously, thus reducing time in the testing cycles.
6. Ballerina
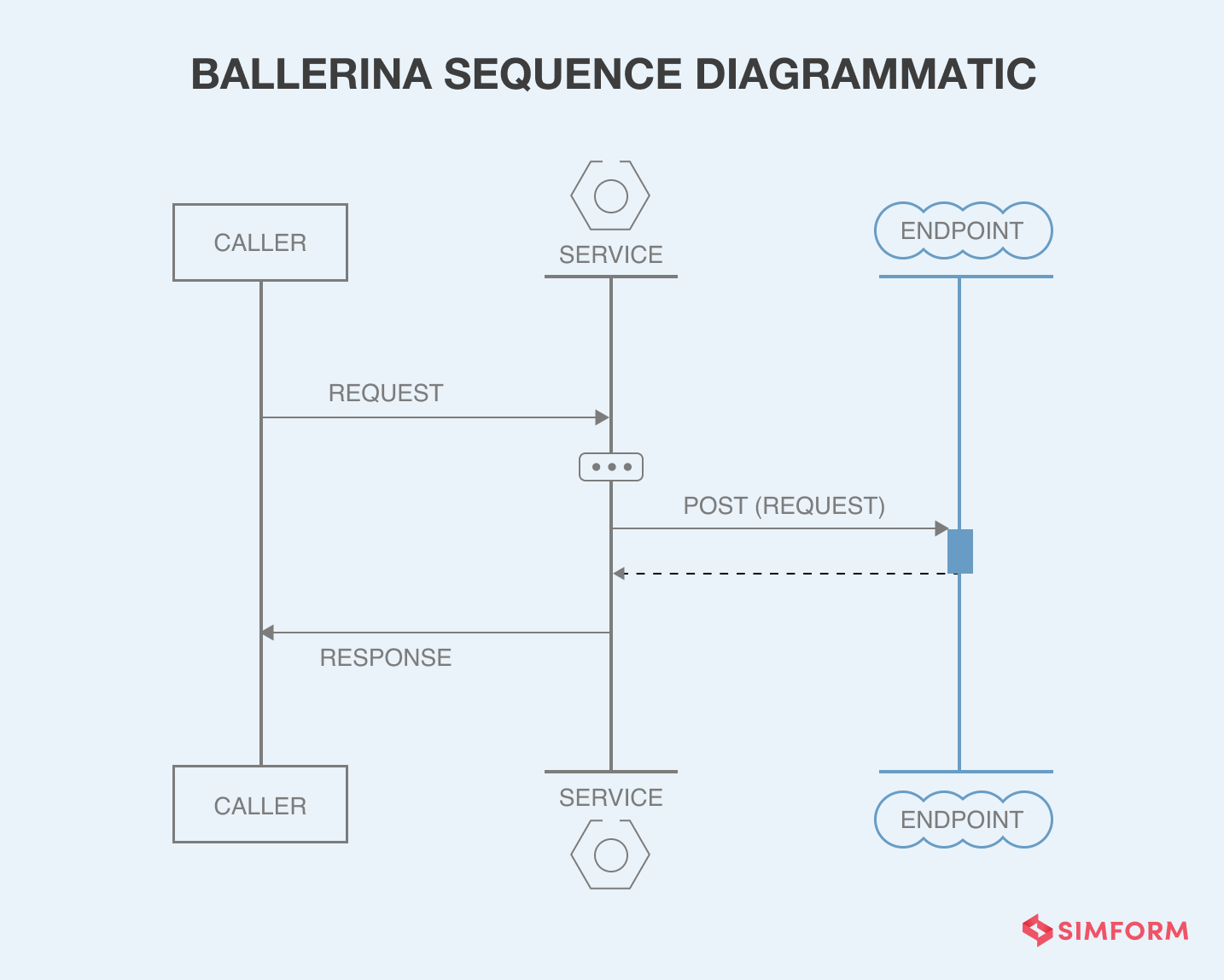
Moving away from traditional microservices frameworks, Ballerina is a distributed programming language for writing distributed systems. It is an open-source programming language that is native to the cloud. Moreover, it is a structural style language that gives developers the flexibility for static typing within the program and describing its service interfaces.
Ballerina is data-oriented, graphical, and concurrent in nature, allowing devs to build a decoupled system from scratch. It’s designed to create network applications and systems that can provide networking services.
Ballerina fits within the modern application development lifecycle despite being a specific system with definitive requirements. With its built-in tools, it can easily integrate CI/CD tools, observing and monitoring tools, and cloud orchestration systems. It even has an intuitive feature of alerting the developers about possible security threats, network failures, and communication gaps while devs are typing the codes for seamless deployment services in the later stages.
Key Benefits:
- Interactive design through visual representations, making it easy to understand.
- Makes the best use of diagrams for all-round integration.
- Increased flexibility for developers to write codes in both Swagger and Ballerina.
7. Oracle Helidon
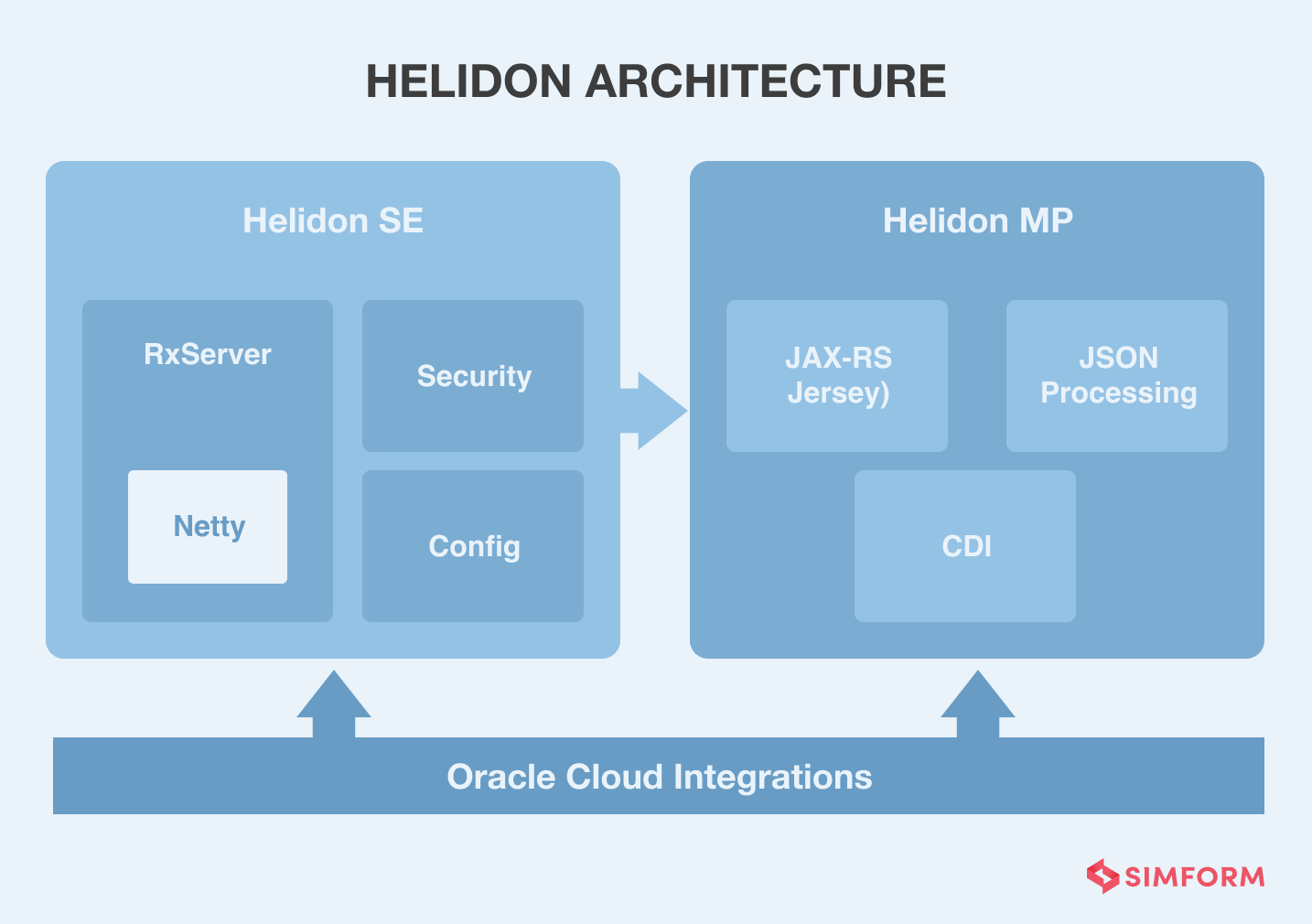
With lightweight and fast app development features, Helidon is slowly taking over the microservices market. It is an open-source cloud-native set of Java libraries that run on the fast web and is powered by Netty. The Helidon Reactive WebServer makes this library a functional programming model.
As Helidon is a declarative programming model with cloud-native features, it has multiple features that set it apart from its competitors. For example, it has full Eclipse MicroProfile support, CDI support, and database support that includes GraphQL, CORS, and gPRC. Plus, it has the minimal memory footprint with a minimum of 70 MB with Helidon and GraalVM Native and consumes a disk space of 92 MB with the same integration model.
Oracle Helidon supports APIs like JAX-RS, CDI, JSON-P/B, making applications fast and responsive. Moreover, being a collection of Java libraries running on a Netty core, there is no extra overhead or bloat for an application that devs face while using other frameworks. Health checks and metric observability tools support integration with Prometheus, Jaeger/Zipkin, and Kubernetes. Furthermore, with GaalVM Native Image Support, you can even compile your Helidon apps into small native executable files, as a jlink image, or as a traditional JAR application.
Key Benefits:
- The lowest startup time ranging from 0.09 seconds to 2.03 seconds.
- Consists of an extensive cloud-native ecosystem with all the necessary and universal technology support.
- Consists of two variants for definitive programming requirements – Helidon SE and Helidon MP.
8. Moleculer
Moleculer is an open source Node.js microservices framework licensed under MIT and contains most of all important microservices features such as service registry, auto-discovery, load balancing, circuit-breaker, bulkhead and fallback response.
Key Benefits:
- It has excellent documentation, where you can learn the concepts, the transport layer for inter-service communication like (TCP, NATS, MQTT, Redis, NATS Streaming, Kafka, AMQP 0.9, AMQP 1.0) and all the other steps to get it up and running.
- It supports both RPC and event-driven architectures and has built-in caching, data validation,and much more.
- Moleculer’s mixins are one of its best resources. It distributes reusable functionality in a single place for all services, but is available from any service at any time.
9. AxonIQ
Axon Framework, developed by AxonIQ, is a Java microservices framework well-suited for implementing key architectural concepts like Event Sourcing, Command Query Responsibility Segregation (CQRS), and Domain-Driven Design (DDD).
Axon offers a cohesive and efficient approach for building Java applications to transition from monolithic structures to Event-Driven microservices smoothly. This transition is enabled via two main components: the Axon Framework, which provides a versatile programming model, and Axon Server, which handles infrastructure support. Both of these components are open-source.
Key Benefits:
- Axon is equipped to meet the most demanding enterprise needs, offering efficient event storage scaling, robust security measures, clustering capabilities, load balancing, and service discovery.
- It also supports globally distributed data centers, seamless integration with third-party services, and comprehensive metrics and monitoring..
10. Lagom
Lagom is an open-source framework designed to develop Reactive microservices in Java or Scala. It has capabilities of Akka and Play, which are reliable technologies used in demanding applications.
One of Lagom’s key features is its integrated development environment, which simplifies the process of building microservices. With just a single command, developers can compile the project, initiate necessary components and microservices, and set up the Lagom infrastructure. This environment also offers hot-reloading, automatically updating the project when it detects changes in the source code.
Key Benefits:
- Lagom’s approach to creating appropriately-sized services has several advantages. It clarifies development responsibilities, enhancing agility.
- It promotes more frequent releases with reduced risk, thereby speeding up time-to-market.
- Lagom helps build systems with reactive characteristics, including responsiveness, resilience, scalability, and elasticity, all of which are crucial for optimizing modern computing environments and meeting high user expectations.
Comparing the Chosen Microservices Frameworks
| FRAMEWORK | LANGUAGE | GITHUB POPULARITY | BUILD TOOLS | HOT RELOAD | LOAD BALANCING |
| Spring Boot | Java | 69.7k | Mavel and Gradle | Yes | Spring Cloud Load Balancer |
| Golang | Go | GoMicro- 20.9k
Gokit- 25.5k |
Module aware toolkit that can integrate standard modules tooling. | No | Integration with external load balancers |
| Eclipse Vert.x | Polyglot | 13.8k | Maven | Yes | Vert.X TCP Server |
| Quarkus | Java | 12.4k | Mavel and Gradle | Yes | Small Rye Stork |
| Micronaut | Polyglot | 5.8k | Gradle, Gradle Kotlin, and Maven | No | Netflix Ribbon |
| Ballerina | Ballerina | 3.4k | Ballerina CLI | No | HTTP load balancing endpoint |
| Oracle Helidon | Java | 3.2k | Helidon CLI | No | Apache httpd load balancer |
| Moleculer | JavaScript | 5.9k | Moleculer CLI | Yes | A built-in service registry and round robin load balancer |
| AxonIQ | Java | 3.1k | Maven, Gradle and Spring Boot | No | External load balancer such as NGINX, HAProxy or cloud provider load balancers like ELB |
| Lagom | Java, Scala | 2.6k | SBT (Scala build tool) | Yes | Akka clustering and Distributed Data router for internal load balancing |
Choosing the Best Microservices Frameworks
While these frameworks might have similar characteristics and standards, the right apps are to be built around business capabilities, and this can only be achieved with an appropriate framework in place. For instance, there is a wide variety of programming languages, in-built key features for specific applications, database support, ease of integration, and much more to consider.
Here is a list of questions you need to think about before choosing a microservices framework for your application.
- Does your microservice framework have built-in support for observable application metrics, health checks, and analytics?
- Does your framework support standard or necessary APIs and technology required for the application development process?
- Does your framework support automation and allow integration of automation tools for improved development time and speed?
- Does your microservice framework support independent deployment over a distributed system?
- Does your framework have decentralized components, and can it be customized separately?
- Does your microservice framework support continuous integration, deployment, and continuous delivery (CI/CD) and allow integration of CI/CD tools for enabling DevOps?
- Can the selected framework scale with changing business models or requirements?
- Can the microservice framework carry out and run unit testing while the dev writes the codes?
- Does the framework support the necessary database that you deem powerful for your application?
Microservices is the backbone of a modern application with more efficiency, productivity, delivery, and speed. Choosing the proper framework requires an eye for detail and expertise to claim that the selected framework would deliver the expected outcomes.
Our cloud development team of experts at Simform knows that way through the intricacies of microservices and is highly skilled in taking any business to new heights. Consult with us today for implementing a new microservices framework for your budding business.